What is mold?
« Mold » is the general term used to designate microscopic fungi, which are generally organisms that live from the assimilation of decomposed organic matter.
Learn moreMold Testing Laboratory

Bien qu’il soit généralement aisé de détecter des moisissures à l’œil nu ou par l’odeur, il est parfois nécessaire d’effectuer des analyses en laboratoire pour déterminer l’étendu de l’infestation afin de prévoir des traitements et réparations appropriés de la surface atteinte. Sur le plan médical, ces analyses sont intéressantes lorsque des familles souffrent de maladies pouvant provenir d’une contamination fongique, notamment si le milieu est propice au développent des moisissures. Les analyses sont également un moyen non invasif de s’assurer de l’absence de moisissures dans un immeuble avant d’en procéder à l’acquisition. Finalement, des analyses approfondies peuvent être requises en tant que preuve légale en cas de conflit ou de vice caché.

La première méthode consiste à prélever des échantillons et de les mettre en culture afin de détecter la présence de moisissures et d’en déterminer le type et la quantité. Les échantillons sont prélevés aussi bien sur les moisissures que sur les poussières ambiantes. Cette méthode dite « viable » nécessite souvent environ 15 jours. La deuxième méthode est une étude microscopique classique. Elle consiste à prélever des échantillons d’air, de matière ou de surface, de les colorer et ensuite de les examiner sous un microscope à lumière transmise pour déterminer la présence ou non de spores ou de particules mycosiques et en déterminer l’espèce le cas échéant. Cette méthode, appelée « non viable » permet généralement de donner des résultats en moins d’une semaine. Une fois la contamination traitée, il est utile de procéder à une deuxième analyse microscopique qui permettra de s’assurer que les moisissures ont été totalement éliminées et les surfaces sont a nouveau saines.

Axxonlab propose un service de détection de la présence de moisissures au moyen des deux méthodes, celle de la mise en culture d’échantillons et celle de la microscopie à lumière transmise. Les résultats sont disponibles sous 24 ou 48 heures ; sous certaines conditions il est possible d’obtenir les résultats le jour même des prélèvements
What is mold?

« Mold » is the general term used to designate microscopic fungi, which are generally organisms that live from the assimilation of decomposed organic matter. They are brought indoors by drafts, pets and humans. Mold develops in humid areas where the temperatures vary from 2° C to 40° c (35°F to 104° F) and where there are available nutriments like food products (fruit, vegetables, pet foods…) carpets and rugs, books and documents, damp clothing or cloth, organic glues and coatings, wood, cardboard, and plaster blocks. Mold is often found in basements, kitchens, and bathrooms, as well as in storage areas, behind furniture or in bookcases, especially if ventilation is insufficient. It can also be found on other moist surfaces such as walls and window frames where humidity from leaks or condensation is present.
There are thousands of species of mold. Penicillium, which is the basis for penicillin, is one of them; aspergillum, which causes a respiratory disease, is another. Mold can be detected by the presence of blackish or brownish spots on the infested surfaces, a distinctive moldy, earthy or alcoholic smell, and detachment, deformity or other signs of water infiltration that indicate the presence of mold colonies under the materials.
It is usually easy to prevent the development of mold by ensuring proper air circulation in rooms and by storing linens, cardboard, plaster blocks, wood or other porous materials in correctly ventilated areas. Dryer vents should be correctly installed and checked, humidifiers properly cleaned, and any damage from leaks should be repaired immediately. Careful attention to cleanliness is necessary, especially in the rooms where humidity is present. If the mold is discovered, it can be treated with appropriate products, the infested spot cleaned and properly dried, and the contaminated materials removed and disposed of. Should the infestation be critical, or the building structure affected, it is necessary to get assistance from a specialist to eliminate the mold.
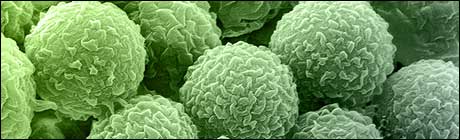
If present in small quantities, and regularly treated and eliminated, mold is not a serious health hazard. On the other hand, if there are large, uncontrollable colonies, the mold releases tiny particles into the surrounding air. These particles, if inhaled, can by highly toxic. Since the 1980’s, the authorities in several countries, in particular in North America and Europe, have become concerned about the increase in the number of cases of mold-related pathologies. Spores and mold dust can cause allergies and other respiratory problems in sensitive patients, trigger asthma attacks, and even be the cause of potentially deadly diseases. Some mold produces mycotoxins in certain environmental conditions, particularly in the industrial and agricultural sectors, where the combination of chemical or phytosanitary products and mold can lead to very serious health issues.
Long-term indoor exposure to air that is polluted by spores and mold dust can lead to serious lung disease and cause cancers or hepatotoxic, neurotoxic, mutagenic and immunosuppressive pathologies. This is the case when patients have been exposed to Stachybotrys, or toxic black mold, which causes severe health problems especially in families and young children living in dilapidated housing that cannot be properly sanitized. Symptoms are allergic reactions, nausea, vomiting, dizziness and even pulmonary bleeding, and severe cases can be fatal. Aspergillum sometimes affects patients in poor health and can be found in hospitals as a nosocomial disease. It can also cause death if the patient is severely immunodeficient. Other types of fungi can be found in bird droppings and can cause a sickness similar to influenza. Finally, food contaminated by mold can lead to food poisoning the gravity of which depends on the fragility of the person and the quantity of mold consumed.